 CAR‑T cell therapy is a groundbreaking form of immunotherapy that uses a patient’s T-cells, which are modified to recognize and attack cancer cells. With the advent of the genomic era, we now have the tools to personalize and enhance these treatments, enabling us to target cancers that were once deemed incurable. In our discussion, we will break down the science behind CAR‑T therapies, highlight recent advancements, and provide a clear look into how these innovations are reshaping cancer care.
CAR‑T cell therapy is a groundbreaking form of immunotherapy that uses a patient’s T-cells, which are modified to recognize and attack cancer cells. With the advent of the genomic era, we now have the tools to personalize and enhance these treatments, enabling us to target cancers that were once deemed incurable. In our discussion, we will break down the science behind CAR‑T therapies, highlight recent advancements, and provide a clear look into how these innovations are reshaping cancer care.

Over the past decade, the field of immunotherapy has evolved rapidly. Early forms of CAR‑T cell therapy focused on a single target, but researchers soon recognized the need for more adaptable and precise approaches. Today, the integration of genomic data has allowed us to fine-tune these treatments, leading to better outcomes for patients with complex and multi‑refractory cancers.
Understanding CAR‑T Cell Therapy
CAR stands for Chimeric Antigen Receptor. In simple terms, this is a protein that is added to T-cells to help them identify and attack cancer cells. We collect T-cells from the patient, engineer them in a laboratory to express these receptors, and then reintroduce them into the patient’s bloodstream. Once inside, these modified cells seek out and destroy cancer cells that express the targeted antigens.
The Genomic Era and Its Impact on Cancer Treatment
The genomic era has ushered in a new level of precision in cancer therapy. By analyzing a patient’s genetic makeup and the molecular profile of their tumor, we can customize CAR‑T cell therapy to be more effective. This integration of genomics not only helps in selecting the best target antigens but also improves the safety and efficacy of the treatment.
To fully appreciate the power of CAR‑T cell therapy, it is important to understand its process. The journey from cell collection to cancer cell destruction is both intricate and fascinating.
Collection and Modification
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Collection | Extraction of T-cells from the patient’s blood |
| Engineering | Genetic modification to express chimeric antigen receptors |
| Expansion | Laboratory growth to increase cell numbers |
| Infusion | Reintroduction of modified T-cells into the patient’s body |
Table: The CAR‑T Cell Therapy Process
Mechanism of Action
Once infused, the CAR‑T cells locate cancer cells by recognizing specific markers on their surface. They then bind to these cells and initiate a potent immune response that results in the targeted destruction of the cancer cells. This process can lead to dramatic clinical responses, even in patients who have exhausted other treatment options.

Recent advancements in the engineering of CAR‑T cells have significantly improved their effectiveness, especially for patients with multi‑refractory cancers.
Innovations in CAR Design
Researchers have made major strides by developing CARs that target multiple antigens simultaneously. This dual or even multi‑target approach reduces the risk of cancer cells evading detection. Additionally, improvements in the CAR design have enhanced the cells’ ability to survive and proliferate in the body, which is essential for long-term remission.
Genomic Data and Precision Medicine
The incorporation of genomic data into CAR‑T cell therapy has paved the way for precision medicine. By identifying unique genetic markers in tumors, we can design CAR‑T cells that are specifically tailored to an individual’s cancer profile. This customization increases the chances of treatment success and minimizes potential side effects.
Multi‑refractory cancers, which have not responded to multiple lines of therapy, present a significant challenge. However, advanced CAR‑T cell therapies offer a new beacon of hope for these patients.
Understanding Multi‑Refractory Cancers
Multi‑refractory cancers are characterized by their resistance to conventional treatments such as chemotherapy, radiation, and targeted therapies. These cancers often have complex genetic profiles that allow them to adapt and survive despite multiple treatment attempts. Advanced CAR‑T cell therapies are designed to overcome these defense mechanisms by using a patient’s own immune cells, engineered to seek and destroy even the most resilient cancer cells.
Clinical Success Stories
Several clinical studies have reported promising results using advanced CAR‑T cell therapies in patients with multi‑refractory cancers. These studies highlight not only the potential of CAR‑T cells to induce remission but also their role in extending patient survival. While challenges remain, the successes seen so far provide a strong foundation for future research and broader clinical application.
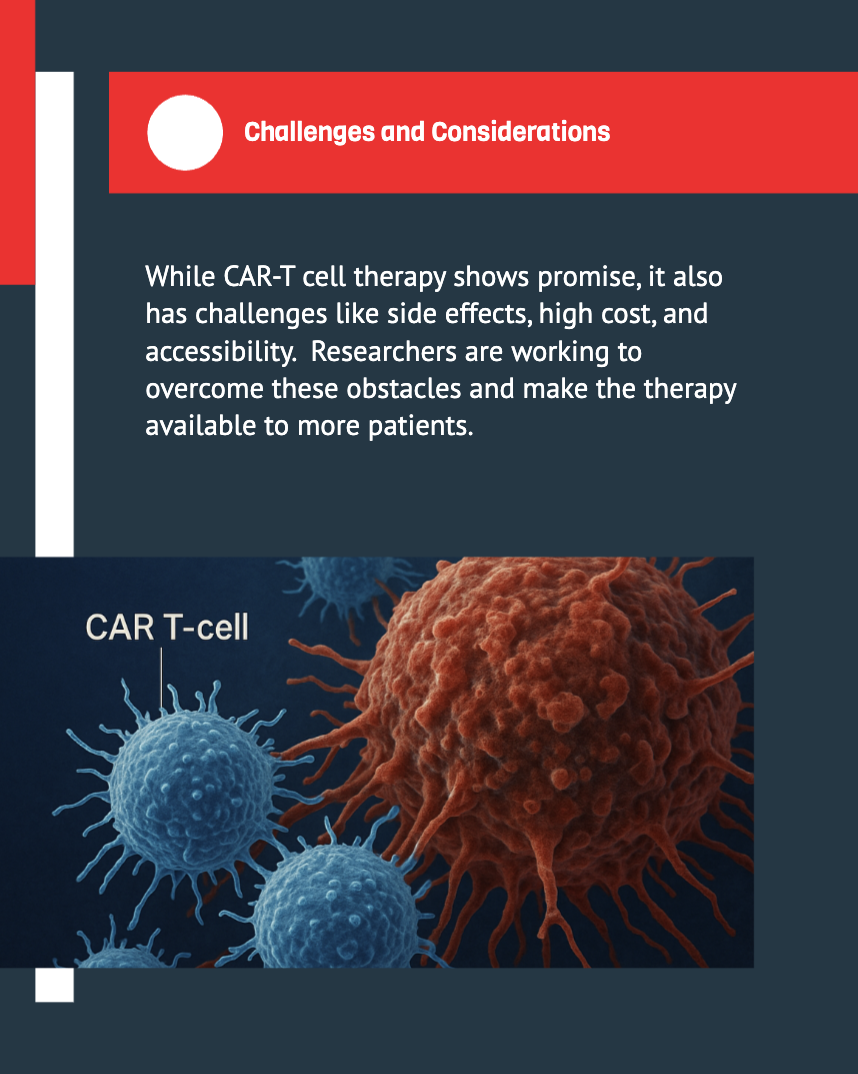
Despite its promise, CAR‑T cell therapy comes with its own set of challenges. Understanding and managing these issues is crucial for the continued advancement and accessibility of the treatment.
Managing Side Effects and Safety
One of the primary concerns with CAR‑T cell therapy is the risk of side effects such as cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and neurotoxicity. CRS occurs when the infused T-cells release large amounts of cytokines, leading to inflammation and other potentially severe symptoms. Advances in monitoring and management strategies have improved the safety profile of CAR‑T therapies, but ongoing research is essential to further reduce these risks.
Cost and Accessibility
The complexity of the manufacturing process and the need for highly specialized facilities contribute to the high cost of CAR‑T cell therapy. Ensuring that these treatments are accessible to a broader patient population remains a significant hurdle. Researchers and policymakers are actively exploring ways to streamline production and reduce costs without compromising the quality and efficacy of the therapy.
As we look ahead, the future of CAR‑T cell therapy is filled with exciting possibilities. Continuous innovation in genetic engineering and immunotherapy is set to further enhance treatment outcomes.
Next‑Generation CAR‑T Cells
The next wave of CAR‑T cell therapies includes the development of “armored” CAR‑T cells that are engineered to overcome the hostile tumor microenvironment. These cells are designed to resist the suppressive signals from cancer cells, thereby increasing their survival and effectiveness. Researchers are also exploring the use of CRISPR and other gene-editing technologies to further refine these treatments.
Combining CAR‑T Therapy with Other Treatments
Combination therapies are emerging as a promising strategy to enhance the efficacy of CAR‑T cell therapy. By integrating CAR‑T cells with other forms of immunotherapy—such as checkpoint inhibitors—and traditional treatments, we can create a synergistic effect that improves patient outcomes. The integration of genomic insights further supports the development of these combination approaches, ensuring that each patient receives the most effective treatment regimen based on their unique cancer profile.
Genomic data plays a pivotal role in shaping the future of CAR‑T cell therapy. By providing detailed information about the genetic makeup of both the tumor and the patient, genomic analysis enables a more personalized and targeted approach to treatment.
Personalized Treatment Plans
Every cancer is unique, and the use of genomic data allows us to tailor CAR‑T cell therapy to each patient’s specific needs. Personalized treatment plans, informed by genomic insights, ensure that the modified T-cells are optimally designed to recognize and attack the patient’s cancer cells. This level of customization not only enhances the efficacy of the treatment but also minimizes potential side effects.
Advancements in Data Analysis
The rapid evolution of data analysis tools has been instrumental in advancing CAR‑T cell therapy. High‑throughput sequencing and bioinformatics enable researchers to identify key genetic markers that can be targeted by CAR‑T cells. This integration of data science with clinical research accelerates the development of new therapeutic strategies and supports more informed decision‑making in treatment planning.

As advanced CAR‑T cell therapies continue to evolve, it is important to address regulatory, ethical, and patient-related considerations to ensure that these treatments are safe, effective, and accessible.
Regulatory Oversight and Approvals
Regulatory agencies play a crucial role in overseeing the development and approval of new CAR‑T cell therapies. Strict guidelines ensure that these treatments meet rigorous safety and efficacy standards before they are made available to patients. Ongoing collaboration between researchers, clinicians, and regulators is essential to keep pace with rapid innovations and to maintain public trust in these therapies.
Patient Experiences and Quality of Life
The impact of CAR‑T cell therapy extends beyond clinical outcomes. Many patients experience a significant improvement in their quality of life following treatment. Through enhanced symptom management and personalized care, advanced CAR‑T cell therapies offer renewed hope for patients who have faced long battles with multi‑refractory cancers. Our approach emphasizes clear communication, compassionate care, and continuous support to ensure that patients receive the best possible experience throughout their treatment journey.
Comparative Analysis: CAR‑T Cell Therapy vs. Other Immunotherapies
To provide a clear picture of where CAR‑T cell therapy stands in the broader landscape of cancer treatments, we have prepared a comparative analysis that highlights key differences between CAR‑T cell therapy and other immunotherapies.
| Feature | CAR‑T Cell Therapy | Checkpoint Inhibitors | Cancer Vaccines |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | Genetically modified T‑cells attack cancer cells | Block proteins that stop the immune system | Stimulate the body’s immune response to cancer |
| Customization | Highly personalized based on genomic insights | More standardized with broad applications | Varies widely with vaccine design |
| Efficacy | Promising for multi‑refractory cancers and precision therapy | Effective in select cancer types with a diverse response | Currently under investigation for broader use |
Table: Comparative Analysis of CAR‑T Cell Therapy and Other Immunotherapies
The success of advanced CAR‑T cell therapies is not solely due to breakthroughs in genetic engineering; it also stems from the collaborative efforts of various disciplines.
Collaborative Research and Innovation
Our progress in CAR‑T cell therapy is driven by the synergy between oncologists, geneticists, bioinformaticians, and clinical researchers. This multidisciplinary approach ensures that every aspect of the therapy—from design and testing to clinical application—is thoroughly optimized for the best possible outcomes.
Future Clinical studies and Expanding Horizons
The road ahead involves more comprehensive clinical studies that encompass diverse patient populations. By continuously refining our approach and incorporating feedback from real‑world experiences, we aim to expand the applicability of CAR‑T cell therapy and make it accessible to a larger group of patients battling multi‑refractory cancers.
While the promise of advanced CAR‑T cell therapies is immense, it is essential that we navigate the ethical landscape responsibly. Patient safety, informed consent, and equitable access are paramount as we push the boundaries of what is possible in cancer treatment.
Ensuring Ethical Practices
As we develop these therapies, ethical considerations guide every decision—from clinical trial design to the distribution of treatment resources. We work closely with ethical boards and regulatory bodies to ensure that our practices not only meet but exceed current standards.
Fostering Patient-Centered Communication
We believe that transparent and compassionate communication is key to effective cancer care. By keeping patients informed and involved in every step of the process, we foster a sense of trust and partnership that is vital for achieving the best clinical outcomes.

Key Takeaways
Advanced CAR‑T cell therapies represent a transformative leap in the fight against multi‑refractory cancers. By integrating genomic data with cutting‑edge genetic engineering, we have opened new avenues for personalized cancer treatment. While challenges such as side effects, cost, and access remain, our continuous research and collaborative efforts promise a future where even the most resilient cancers can be effectively targeted and managed. As we move forward, our commitment is to refine these therapies, ensure patient safety, and ultimately, improve the quality of life for those battling cancer.
1. What is CAR‑T cell therapy?
CAR‑T cell therapy is an innovative treatment that uses a patient’s own T-cells, which are genetically modified to recognize and attack cancer cells. This personalized approach helps in targeting cancer that has become resistant to conventional treatments.
2. How does genomic data enhance CAR‑T cell therapy?
Genomic data allows us to understand the unique genetic makeup of a patient’s tumor. This information helps us design CAR‑T cells that are precisely tailored to target specific cancer antigens, thereby improving treatment outcomes and minimizing side effects.
3. What are the common side effects associated with CAR‑T cell therapy?
Some patients may experience side effects such as cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and neurotoxicity. However, ongoing research and improved management protocols are continuously reducing these risks, making the therapy safer over time.
4. Can CAR‑T cell therapy be combined with other treatments?
Yes, combining CAR‑T cell therapy with other treatments, such as checkpoint inhibitors or traditional therapies, can create a synergistic effect. This combination approach is being actively explored to further enhance the efficacy of cancer treatment.
5. What does the future hold for advanced CAR‑T cell therapies?
The future of CAR‑T cell therapies is promising, with ongoing research focused on next‑generation modifications, combination therapies, and broader applications across various cancer types. Continuous advancements in genomic analysis and gene‑editing techniques are paving the way for more personalized and effective treatments.
 25.03.2025
25.03.2025